Page 21 - Module_5_en
P. 21
Module
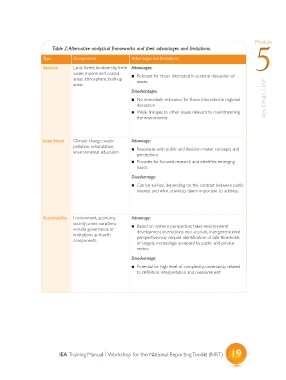
Table 2: Alternative analytical frameworks and their advantages and limitations.
Type Components Advantages and limitations 5
Sectoral Land, forest, biodiversity, fresh Advantages:
water, marine and coastal ? Relevant for those interested in sectoral discussion of
areas, atmosphere, built-up issues.
areas
Disadvantages:
? No immediate relevance for those interested in regional Abu Dhabi, UAE
discussion.
? Weak linkages to other issues relevant to mainstreaming
the environment.
Issue based Climate change, water Advantage:
pollution, urbanization, ? Resonates with public and decision-maker concepts and
environmental education
perceptions
? Provides for focused research and identifies emerging
issues.
Disadvantage:
? Can be ad-hoc, depending on the contrast between public
interest and what scientists deem important to address.
Sustainability Environment, economy, Advantage:
society; some variations ? Based on systems perspective; takes environment/
include governance or development interactions into account; intergenerational
institutions as fourth perspective; may require identification of safe thresholds
components. or targets; increasingly accepted by public and private
sector.
Disadvantage:
? Potential for high level of complexity; uncertainty related
to definition, interpretation and measurement.
IEA Training Manual Workshop for the National Reporting Toolkit (NRT) 19