Page 13 - Module_4_en
P. 13
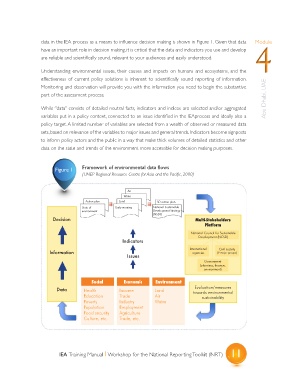
data in the IEA process as a means to influence decision making is shown in Figure 1. Given that data Module
have an important role in decision making, it is critical that the data and indicators you use and develop
are reliable and scientifically sound, relevant to your audiences and easily understood. 4
Understanding environmental issues, their causes and impacts on humans and ecosystems, and the
effectiveness of current policy solutions is inherent to scientifically sound reporting of information.
Monitoring and observation will provide you with the information you need to begin the substantive
part of the assessment process. Abu Dhabi, UAE
While “data” consists of detailed neutral facts, indicators and indices are selected and/or aggregated
variables put in a policy context, connected to an issue identified in the IEAprocess and ideally also a
policy target. A limited number of variables are selected from a wealth of observed or measured data
sets, based on relevance of the variables to major issues and general trends. Indicators become signposts
to inform policy actors and the public in a way that make thick volumes of detailed statistics and other
data on the state and trends of the environment more accessible for decision making purposes.
Figure 1 Framework of environmental data flows
(UNEP Regional Resource Centre for Asia and the Pacific, 2000)
Air
Water
Action plan Land SD action plan
State of Early warning National Sustainable
environment Development Strategy
(NSDS)
Decision Multi-Stakeholders
Platform
National Council for Sustainable
Development (NCSD)
Indicators
International Civil society
Information agencies (9 major groups)
Issues
Government
(planning, finance,
environment)
Social Economic Environment
Evaluation/measures
Data Health Income Land towards environmental
Education Trade Air sustainability
Poverty Industry Watre
Population Employment
Food security Agriculture
Culture, etc. Trade, etc.
IEA Training Manual Workshop for the National Reporting Toolkit (NRT) 11