Page 27 - Module_9_en
P. 27
Step 2: Impacts Module
What are the consequences for the environment and humanity?
Induced by the drivers and caused by pressures, the state of the environment (the physical, chemical or
biological components of the Earth systems, biosphere, basins, etc.) impacts the normal functioning of
ecosystems and the welfare of human beings. Environmental and other impacts are indeed ecosystem-
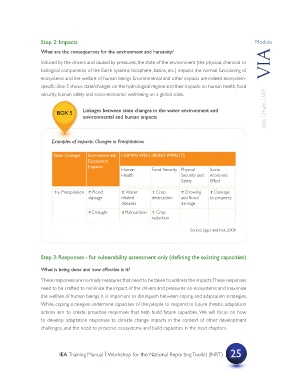
specific. Box 5 shows state/changes on the hydrological regime and their impacts on human health, food
Abu Dhabi, UAE
security, human safety and socio-economic well-being on a global scale.
Linkages between state changes in the water environment and
BOX 5
environmental and human impacts
Examples of impacts: Changes in Precipitations
State Changes Environmental/ HUMAN WELL-BEING IMPACTS
Ecosystem
Impacts
Human Food Security Physical Socio-
Health Security and economic
Safety Effect
?? Precipitation ? Flood ? Water ? Crop ? Drowing ? Damage
damage related destruction and flood to property
diseases damage
? Draught ?Malnutrition ? Crop
reduction
Source: J?ger and Kok, 2008
Step 3: Responses - for vulnerability assessment only (defining the existing capacities)
What is being done and how effective is it?
These responses are normally measures that need to be taken to address the impacts. These responses
need to be crafted to minimize the impact of the drivers and pressures on ecosystems and maximize
the welfare of human beings. It is important to distinguish between coping and adaptation strategies.
While, coping strategies undermine capacities of the people to respond to future threats, adaptation
actions aim to create proactive responses that help build future capacities. We will focus on how
to develop adaptation responses to climate change impacts in the context of other development
challenges, and the need to preserve ecosystems and build capacities in the next chapters.
IEA Training Manual Workshop for the National Reporting Toolkit (NRT) 25