Page 12 - Madagascar Report
P. 12
living in the exposed coastal zones. Poverty, over-reliance on rain-fed agriculture affect livelihoods
making them more vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Strategies to strengthen resilience
and improve the livelihoods of vulnerable households are called for.
The situation
Extreme climate events
Madagascar is one of the African countries most severely affected by climate change impacts and
Country Profile
experiences an average of 3 cyclones per year. Other disasters that the country experiences include
droughts, floods, earthquakes, and locust invasions leading to severe economic losses impacting
human wellbeing. For instance, three cyclones in 2008 affected 342,000 people and caused
an estimated US $333 million in disaster-related damages and losses, equivalent to 4 per cent of
The Republic of Madagascar
GDP. These disasters are becoming more frequent and intense, affecting food security, drinking water
supply and irrigation, human wellbeing and the environment management (GFDRR, 2020).
The constraints
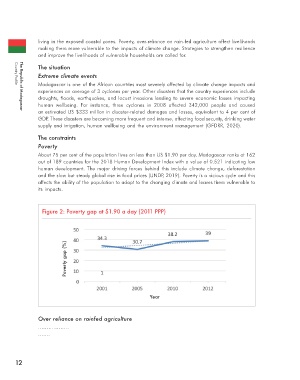
Poverty
About 75 per cent of the population lives on less than US $1.90 per day. Madagascar ranks at 162
out of 189 countries for the 2018 Human Development Index with a value of 0.521 indicating low
human development. The major driving forces behind this include climate change, deforestation
and the slow but steady global rise in food prices (UNDP, 2019). Poverty is a vicious cycle and this
affects the ability of the population to adapt to the changing climate and leaves them vulnerable to
its impacts.
Figure 2: Poverty gap at $1.90 a day (2011 PPP)
Poverty gap (%)
Year
Over reliance on rainfed agriculture
………………
…….
12