Page 105 - Module_5_en
P. 105
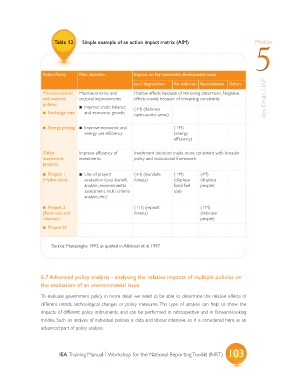
Table 12 Simple example of an action impact matrix (AIM) Module
5
Action/Policy Main objective Impacts on key sustainable development issues
Land degradation Air pollution Resettlement Others
Macroeconomic Macroeconomic and Positive effects because of removing distortions, Negative
and sectoral sectoral improvements effects mainly because of remaining constraints Abu Dhabi, UAE
policies ? Improve trade balance
? Exchange rate and economic growth (-H) (deforest
open-access areas)
? Energy pricing ? Improve economic and (+M)
energy use efficiency (energy
efficiency)
Other Improve efficiency of Investment decisions made more consistent with broader
Investment investments policy and institutional framework
projects
? Project 1 ? Use of project (-H) (inundate (+M) (-M)
(Hydro dam) evaluation (cost-benefit forests) (displace (displace
analysis, environmental fossil fuel people)
assessment, multi-criteria use)
analysis, etc.)
? Project 2 (+H) (replant (+M)
(Re-forest and forests) (relocate
relocate) people)
? Project N
Source: Munasinghe 1993, as quoted in Atkinson et al. 1997
6.7 Advanced policy analysis - analysing the relative impacts of multiple policies on
the evaluation of an environmental issue
To evaluate government policy in more detail we need to be able to determine the relative effects of
different trends, technological changes or policy measures. This type of analysis can help to show the
impacts of different policy instruments, and can be performed in retrospective and in forward-looking
modes. Such an analysis of individual policies is data and labour intensive, so it is considered here as an
advanced part of policy analysis.
IEA Training Manual Workshop for the National Reporting Toolkit (NRT) 103