Page 55 - Module_5_en
P. 55
Module
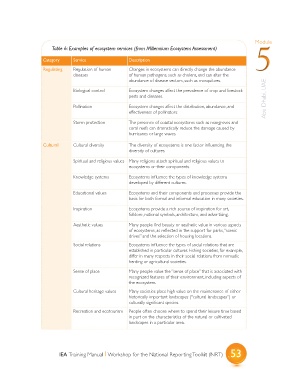
Table 6: Examples of ecosystem services (from Millennium Ecosystem Assessment)
Category Service Description 5
Regulating Regulation of human Changes in ecosystems can directly change the abundance
diseases of human pathogens, such as cholera, and can alter the
abundance of disease vectors, such as mosquitoes.
Biological control Ecosystem changes affect the prevalence of crop and livestock
pests and diseases. Abu Dhabi, UAE
Pollination Ecosystem changes affect the distribution, abundance, and
effectiveness of pollinators.
Storm protection The presence of coastal ecosystems such as mangroves and
coral reefs can dramatically reduce the damage caused by
hurricanes or large waves.
Cultural Cultural diversity The diversity of ecosystems is one factor influencing the
diversity of cultures.
Spiritual and religious values Many religions attach spiritual and religious values to
ecosystems or their components.
Knowledge systems Ecosystems influence the types of knowledge systems
developed by different cultures.
Educational values Ecosystems and their components and processes provide the
basis for both formal and informal education in many societies.
Inspiration Ecosystems provide a rich source of inspiration for art,
folklore, national symbols, architecture, and advertising.
Aesthetic values Many people find beauty or aesthetic value in various aspects
of ecosystems, as reflected in the support for parks, “scenic
drives” and the selection of housing locations.
Social relations Ecosystems influence the types of social relations that are
established in particular cultures. Fishing societies, for example,
differ in many respects in their social relations from nomadic
herding or agricultural societies.
Sense of place Many people value the “sense of place” that is associated with
recognized features of their environment, including aspects of
the ecosystem.
Cultural heritage values Many societies place high value on the maintenance of either
historically important landscapes (“cultural landscapes”) or
culturally significant species.
Recreation and ecotourism People often choose where to spend their leisure time based
in part on the characteristics of the natural or cultivated
landscapes in a particular area.
IEA Training Manual Workshop for the National Reporting Toolkit (NRT) 53