Page 58 - Module_5_en
P. 58
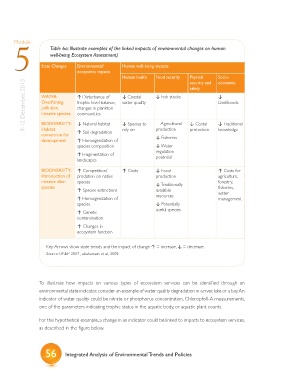
Module Table 6a: Illustrate examples of the linked impacts of environmental changes on human
5 well-being Ecosystem Assessment)
State Changes
Environmental/
ecosystem impacts Human well-being impacts
Human health Food security Physical Socio-
9-12 December, 2013 WATER: ? Disturbance of ? Coastal ? Fish stocks ?
security and
economic
safety
Livelihoods
water quality
trophic level balance,
Overfishing,
changes in plankton
pollution,
communities
invasive species
BIODIVERSITY:
production
rely on
protection
knowledge
Habitat
? Soil degradation
conversion for ? Natural habitat ? Species to ?Agricultural ? Costal ? Traditional
? Fisheries
development ? Homogenization of
species composition ? Water
? Fragmentation of regulation
potential
landscapes
BIODIVERSITY: ? Competition/ ? Costs ? Food ? Costs for
Introduction of predation on native production agriculture,
invasive alien species forestry,
species ? Traditionally fisheries,
? Species extinctions available water
? Homogenization of resources management
species ? Potentially
useful species
? Genetic
contamination
? Changes in
ecosystem function
Key: Arrows show state trends and the impact of change ? = increase, ? = decrease.
Source: UNEP 2007 ; abahussain et al., 2009.
To illustrate how impacts on various types of ecosystem services can be identified through an
environmental state indicator, consider an example of water quality degradation in a river, lake or a bay. An
indicator of water quality could be nitrate or phosphorus concentration, Chlorophyll-A measurements,
one of the parameters indicating trophic status in the aquatic body, or aquatic plant counts.
For this hypothetical example, a change in an indicator could be linked to impacts to ecosystem services,
as described in the figure below.
56 Integrated Analysis of Environmental Trends and Policies