Page 21 - Module_9_en
P. 21
Module
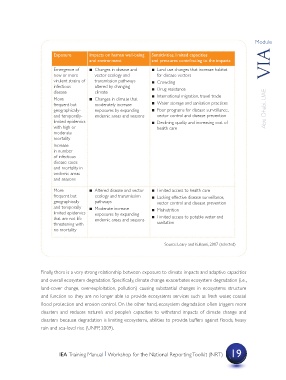
Exposure Impacts on human well-being Sensitivities, limited capacities
and environment and pressures contributing to the impacts
Emergence of ? Changes in disease and ? Land use changes that increase habitat
new or more vector ecology and for disease vectors
virulent strains of transmission pathways ? Crowding
infectious altered by changing ? Drug resistance
disease climate
More ? Changes in climate that ? International migration, travel trade
frequent but moderately increase ? Water storage and sanitation practices
geographically- exposures by expanding ? Poor programs for disease surveillance, Abu Dhabi, UAE
and temporally- endemic areas and seasons vector control and disease prevention
limited epidemics ? Declining quality and increasing cost of
with high or health care
moderate
mortality
Increase
in number
of infectious
disease cases
and mortality in
endemic areas
and seasons
More ? Altered disease and vector ? Limited access to health care
frequent but ecology and transmission ? Lacking effective disease surveillance,
geographically pathways vector control and disease prevention
and temporally ? Moderate increase ? Malnutrition
limited epidemics exposures by expanding
that are not life endemic areas and seasons ? Limited access to potable water and
threatening with sanitation
no mortality
Source: Leary and Kulkarni, 2007 (selected)
Finally, there is a very strong relationship between exposure to climate impacts and adaptive capacities
and overall ecosystem degradation. Specifically, climate change exacerbates ecosystem degradation (i.e.,
land-cover change, over-exploitation, pollution) causing substantial changes in ecosystems structure
and function so they are no longer able to provide ecosystems services such as fresh water, coastal
flood protection and erosion control. On the other hand, ecosystem degradation often triggers more
disasters and reduces nature’s and people’s capacities to withstand impacts of climate change and
disasters because degradation is limiting ecosystems, abilities to provide buffers against floods, heavy
rain and sea-level rise (UNEP, 2009).
IEA Training Manual Workshop for the National Reporting Toolkit (NRT) 19