Page 55 - Module_9_en
P. 55
choices to put resources into adaptation, mitigation or other development priorities. For example, Module
flexible, timber-framed construction is effective in managing subsidence risk but may not cope as well
with overheating and flood risks. Engineering interactions to defend coastlines from flooding and sea-level
rise can also change the connectivity of coastal ecosystems and facilitate the spread of non-native invasive
species. Consequently, the ultimate goal of the adaptation actions is not only to respond to changes in
climatic variables, but also to move towards a resilient community and ecosystems. Using principles of
sustainable development could help in identifying those adaptation responses, creating ancillary benefits
or co-benefits between climate and development goals. For example, extensively using air conditioning
to respond to heat waves, shifting to monocultures of heat resistant crops or building large dykes without
resources for maintenance could be considered unsustainable and maladaptive responses. Abu Dhabi, UAE
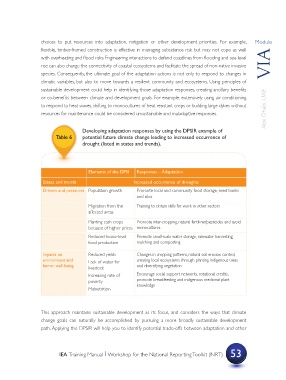
Developing adaptation responses by using the DPSIR example of
Table 6 potential future climate change leading to increased occurrence of
drought (listed in states and trends).
Elements of the DPSI Responses – Adaptation
States and trends Increased occurrence of droughts
Drivers and pressures Population growth Promote local and community food storage, seed banks
and silos
Migration from the Training to obtain skills for work in other sectors
affected areas
Planting cash crops Promote inter-cropping, natural fertilizer/pesticides and avoid
because of higher prices monocultures
Reduced house-level Promote small-scale water storage, rainwater harvesting,
food production mulching and composting
Impacts on Reduced yields Changes in cropping patterns, natural soil erosion control,
environment and Lack of water for creating local ecosystems through planting indigenous trees
human well-being livestock and diversifying vegetation
Increasing rate of Encourage social support networks, rotational credits,
poverty promote breastfeeding and indigenous medicinal plant
knowledge
Malnutrition
This approach maintains sustainable development as its focus, and considers the ways that climate
change goals can naturally be accomplished by pursuing a more broadly sustainable development
path. Applying the DPSIR will help you to identify potential trade-offs between adaptation and other
IEA Training Manual Workshop for the National Reporting Toolkit (NRT) 53