Page 41 - Module_9_en
P. 41
Module
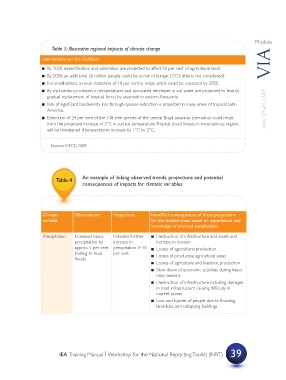
Table 3: Illustrative regional impacts of climate change
Latin America and the Caribbean
? By 2050, desertification and salinization are projected to affect 50 per cent of agricultural lands.
? By 2050, an additional 26 million people could be at risk of hunger (CO2 effects not considered).
? For smallholders, a mean reduction of 10 per cent in maize yields could be expected by 2055.
? By mid-century, increases in temperatures and associated decreases in soil water are projected to lead to
gradual replacement of tropical forest by savannah in eastern Amazonia.
? Risk of significant biodiversity loss through species extinction is projected in many areas of tropical Latin
America. Abu Dhabi, UAE
? Extinction of 24 per cent of the 138 tree species of the central Brazil savannas (cerrados) could result
from the projected increase of 2°C in surface temperature. Tropical cloud forests in mountainous regions
will be threatened if temperatures increase by 1°C to 2°C.
Sources: OECD, 2009
Table 4 An example of linking observed trends, projections and potential
consequences of impacts for climatic variables
Climatic Observations Projections Identified consequences of these projections
variable for the studied areas based on experiences and
knowledge of involved stakeholders
Precipitation Increased heavy Potential further ? Destruction of infrastructure and assets and
precipitation by increase in increase in erosion
approx. 5 per cent precipitation 3–10 ? Losses of agricultural production
leading to local per cent ? Losses of productive agricultural areas
floods
? Losses of agriculture and livestock production
? Slow down of economic activities during heavy
rainy seasons
? Destruction of infrastructure including damages
in road infrastructure causing difficulty in
market access
? Loss and injuries of people due to flooding,
landslides and collapsing buildings
IEA Training Manual Workshop for the National Reporting Toolkit (NRT) 39